Flipped Learning For All Learners: Visual, Auditory, and Kinaesthetic
Introduction

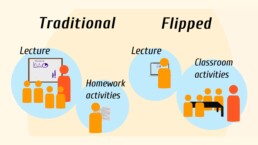
The Flipped Learning model has been gaining popularity in recent years as more and more teachers look for ways to create an engaging and effective learning environment for all students. Flipped Learning is based on the idea that students can learn independently outside of class, freeing up class time for active, hands-on learning experiences.
One of the great things about Flipped Learning is that it can be used with any content, and customized to meet the needs of any learner, including visual, auditory, and kinaesthetic learners.
There are three types of learners we will be discussing: visual, auditory, and kinaesthetic learners. Each type of learner learns best in a different way. Visual learners learn best by seeing things, auditory learners learn best by hearing things, and kinaesthetic learners learn best by doing things.
In a traditional classroom setting, all three types of learners are at a disadvantage since they are all being taught the same way. However, with Flipped Learning, each type of learner can learn in the way that is best for them.
Here’s a closer look at how each type of learner can benefit from Flipped Learning in the classroom.
Visual Learners

Visual learners are those who learn best by seeing information. In a flipped classroom, visual learners can watch lectures or read texts. Additionally, visual learners can take advantage of online resources such as videos, infographics, and charts to supplement their learning.
For visual learners, one of the biggest benefits of Flipped Learning is that it allows them to process information at their own pace. In a traditional classroom setting, visual learners may feel rushed when trying to take in the information presented verbally or auditorily. However, with Flipped Learning, they can pause and rewind videos as needed to make sure they understand the material before moving on. Additionally, many flipped classrooms use digital resources that are highly engaging and visually stimulating, which helps keep visual learners engaged in the material.
Auditory Learners
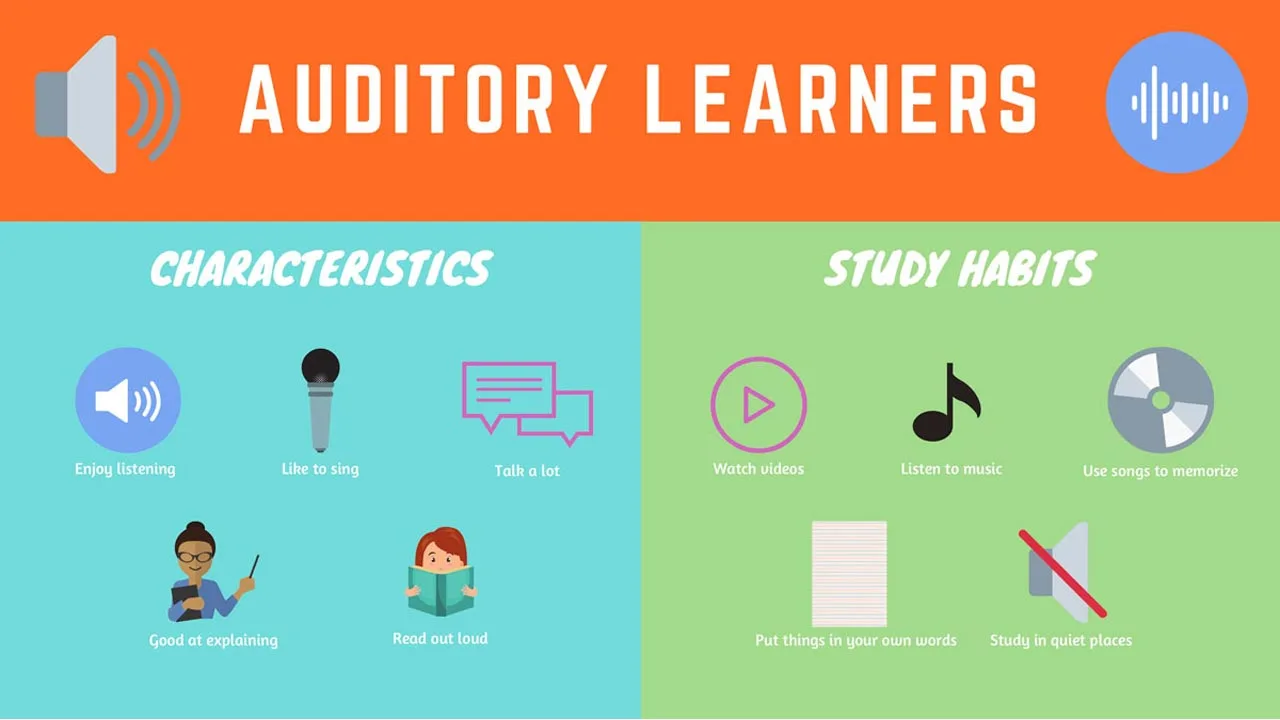
Auditory learners are those who learn best by hearing information. In a flipped classroom, auditory learners can listen to lectures. They can pause, rewind, and review material as needed in order to fully understand the concepts. Additionally, auditory learners can take advantage of online resources such as podcasts and audiobooks to supplement their learning.
Auditory learners can also benefit from the pacing advantages of flipped learning. In addition, auditory learners often thrive in group settings where they can discuss the material with their classmates. Class time in a flipped classroom is typically devoted to group work or other activities that allow auditory learners to process information more deeply by talking through it with their peers.
Kinesthetic Learners

Kinaesthetic learners are those who learn best by doing. In a flipped classroom, kinaesthetic learners thrive best from completing activities and exercises. Additionally, kinaesthetic learners can take advantage of online resources such as simulations and games to supplement their learning.
In a traditional classroom setting, kinaesthetic learners may have trouble sitting still for long periods of time and paying attention to lectures. However, in a flipped classroom, kinaesthetic learners are able to get up and move around while they work on projects or engage in other active learning activities. This increased level of movement helps kinaesthetic learners stay engaged and focused on the task at hand.
Conclusion
A flipped classroom can be an excellent way to engage all types of learners—visual, auditory, and kinaesthetic. By allowing students to consume lectures or readings at home on their own time, they can then come to class ready to engage in discussions and activities that will help them solidify their understanding of the material.
With the right resources, a flipped classroom can be an inclusive learning environment for all students. Give flipped learning a try in your classroom today!