Sponsored ads
3 Ways To Improve Problem-Solving Skills With Flipped Learning Today
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing world, problem-solving skills have become essential for success in various domains. To foster these skills effectively, educators are turning to innovative teaching methodologies like flipped learning.
Flipped learning has gained significant popularity due to its ability to engage students actively and enhance their problem-solving abilities.
In this blog post, we will explore what flipped learning is, why it is an effective approach, different methods to employ in flipped learning for problem-solving skills, and provide actionable recommendations for implementation.
Understanding Flipped Learning

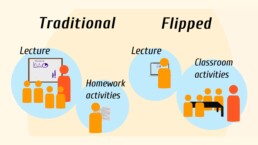
Flipped learning is an instructional strategy that reverses the traditional classroom model. In a flipped classroom, students learn foundational knowledge outside of class through pre-recorded lectures, readings, or online resources, while class time is dedicated to interactive activities, discussions, and problem-solving tasks. This approach allows students to engage in active learning and apply their knowledge to solve real-world problems.
Benefits:
- Active Engagement: Flipped learning promotes active learning and engagement, as students take ownership of their learning process.
- Individualized Pace: Students can learn at their own pace, allowing them to grasp concepts before engaging in problem-solving activities.
- Application of Knowledge: Flipped learning provides opportunities for students to apply their knowledge in practical problem-solving scenarios, improving their problem-solving skills.
Methods for Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills in Flipped Learning

a) Pre-Class Assignments: Assigning videos, readings, or online modules before class helps students acquire foundational knowledge independently. This enables them to use class time for collaborative problem-solving activities or case studies.
b) In-Class Problem-Solving Activities: Use class time to facilitate group discussions, problem-solving exercises, and simulations. Encourage students to work together to analyze and solve complex problems, fostering critical thinking and collaboration skills.
c) Peer Instruction: Incorporate peer instruction techniques, such as think-pair-share or peer feedback sessions. This encourages students to explain their thought processes and learn from each other’s perspectives, enhancing problem-solving abilities.
Effective Implementation of Flipped Learning for Problem-Solving Skills
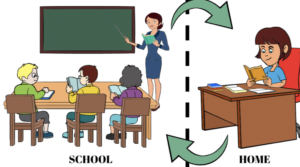
a) Start Small: Begin by flipping specific lessons or topics gradually, allowing students and educators to acclimate to the new approach.
b) Clear Communication: Communicate expectations, goals, and timelines to students and parents/guardians.
c) Monitoring Progress: Regularly assess student comprehension and problem-solving skills to provide timely feedback and support.
d) Provide Resources: Curate or create high-quality resources, such as video lectures, interactive simulations, or online practice problems, to support students’ independent learning.
Actionable Takeaways and Recommendations
a) Emphasize The Why: Clearly communicate the benefits of flipped learning and how it enhances problem-solving skills to motivate students.
b) Promote Collaboration: Encourage collaboration and peer-to-peer learning during in-class problem-solving activities.
c) Build a Supportive Environment: Foster a safe and supportive classroom environment where students feel comfortable taking risks and asking questions.
d) Continuous Professional Development: Teachers should engage in professional development opportunities to enhance their understanding and application of flipped learning strategies.
Conclusion
Flipped learning is a powerful approach that can enhance problem-solving skills by engaging students actively and allowing them to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios.
By leveraging methods such as pre-class assignments, in-class activities, and peer instruction, educators can create an environment that cultivates critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving abilities.
Implementing flipped learning for enhanced problem-solving skills requires careful planning, clear communication, and ongoing support. By following the recommendations provided and adapting them to specific educational settings, educators can empower their students to become confident and proficient problem solvers in the ever-evolving world.